Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) infections, a significant public health concern in China, have been on the rise in recent years, posing a growing threat to the well-being of the population.
Editor's Notes: Research has shown “The Growing Threat Of Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) Infections In China” have published at today date".
After doing an in-depth study, analyzing data, and gathering information from a variety of sources, we have compiled this overview of the "The Growing Threat Of Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) Infections In China" to give you a better grasp of the subject.
FAQ
The growing incidence of human metapneumovirus (hMPV) infections in China poses a significant public health threat. To address concerns and provide clarity, we present a comprehensive series of frequently asked questions (FAQs) that explore this topic in-depth.

Antibiotic resistance: a growing threat to human health - Source www.ecdc.europa.eu
Question 1: What is human metapneumovirus (hMPV)?
Answer: hMPV is a respiratory virus that belongs to the family Pneumoviridae. It primarily infects the respiratory tract, causing symptoms ranging from mild upper respiratory infections to more severe lower respiratory tract infections.
Question 2: How is hMPV transmitted?
Answer: hMPV is primarily spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also be transmitted through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects.
Question 3: Who is at risk for severe hMPV infection?
Answer: Young children, elderly individuals, and those with underlying respiratory conditions are at higher risk for developing severe hMPV infections. Immune-compromised individuals are also at increased risk.
Question 4: What are the symptoms of hMPV infection?
Answer: Symptoms of hMPV infection vary depending on the severity of the infection. Mild infections may cause symptoms similar to the common cold, including runny nose, cough, and fever. Severe infections can lead to pneumonia, bronchiolitis, and other lower respiratory tract infections.
Question 5: Is there a specific treatment for hMPV infection?
Answer: Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment available for hMPV infection. Treatment focuses on supportive care, such as rest, fluids, and medications to relieve symptoms.
Question 6: How can hMPV infections be prevented?
Answer: Preventive measures include regular handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or elbow, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals. Vaccination against hMPV is currently not available.
Understanding the key aspects of hMPV infections is crucial for effective public health measures. As research continues, we remain committed to providing accurate and up-to-date information to address this growing threat.
Transition to the next article section:
Tips
A report from 2021 shows a rapid and persistent surge in Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) infections in China. This poses a pressing threat due to the virus's ability to cause severe respiratory illness, particularly among vulnerable populations like young children and the elderly. To address this growing concern, implementing comprehensive prevention and control measures is crucial.
Tip 1: Vaccination:
Currently, there is no specific vaccine available for hMPV. However, research and development efforts are ongoing to create an effective vaccine that can prevent or reduce the severity of hMPV infections.
Tip 2: Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) Measures:
Implementing effective IPC measures, such as hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette (e.g., covering coughs and sneezes), and environmental cleaning and disinfection, can significantly reduce the transmission of hMPV and other respiratory viruses.
Tip 3: Early Detection and Diagnosis:
Prompt diagnosis of hMPV infections allows for appropriate clinical management and can help prevent severe complications. Diagnostic tests, such as molecular assays or serological tests, can aid in early detection and confirmation of hMPV infections.
Tip 4: Antiviral Treatment:
Currently, there are no specific antiviral treatments approved for hMPV infections. However, research is ongoing to develop effective antiviral therapies that can mitigate the severity and duration of hMPV-associated illness.
Tip 5: Public Health Surveillance:
Strengthening public health surveillance systems is essential for monitoring the incidence, prevalence, and geographic distribution of hMPV infections. This allows for timely detection of outbreaks and implementation of appropriate control measures.
Tip 6: Healthcare Provider Education:
Educating healthcare providers about hMPV infections, including clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management strategies, is crucial. This can enhance the quality of care for patients and contribute to reducing the burden of hMPV infections.
Tip 7: Collaboration and Research:
Collaborative efforts among researchers, public health officials, and healthcare providers are vital for advancing knowledge about hMPV infections, developing preventive and therapeutic interventions, and implementing effective control strategies.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By implementing these measures, China can effectively address the growing threat of hMPV infections and protect the health of its population. Vaccination, IPC, early detection, antiviral treatment, public health surveillance, healthcare provider education, and collaboration are key strategies for combating hMPV infections and minimizing their impact on the Chinese healthcare system and society.
Transition to the article's conclusion:
As the research progresses and more knowledge about hMPV infections is gained, China is well-positioned to develop and implement targeted interventions to address this growing threat effectively. By embracing a comprehensive approach to prevention, surveillance, and treatment, the country can safeguard the health of its citizens and contribute to global efforts in combating hMPV infections.

Capilia™ hMPV | Human Metapneumo virus Rapid Tests | TAUNS Laboratories - Source maxanim.com
The Growing Threat Of Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) Infections In China
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) infections are a significant public health concern, particularly in China, where they pose growing threats to respiratory health. Several key aspects underscore this issue, ranging from the virus's prevalence to the impact on vulnerable populations.
- Prevalence: hMPV infections show an increasing trend, affecting a large number of individuals.
- Seasonality: Infections exhibit seasonal patterns, with outbreaks occurring primarily during winter and spring.
- Age Distribution: Children under five years old bear the highest burden of hMPV infections and severe complications.
- Transmission: The virus spreads through respiratory droplets, facilitated by close contact and poor hygiene.
- Clinical Manifestations: Infections range from mild respiratory symptoms to severe lower respiratory tract illnesses, including bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
- Economic Impact: hMPV infections contribute significantly to healthcare costs, hospitalizations, and work absenteeism.
These aspects highlight the growing threat of hMPV infections in China, emphasizing the need for enhanced surveillance, preventive measures, and robust healthcare systems to mitigate their impact on public health. As research continues to unravel the intricacies of hMPV, further insights into its epidemiology, pathogenesis, and potential interventions will aid in safeguarding the health and well-being of affected communities in China.
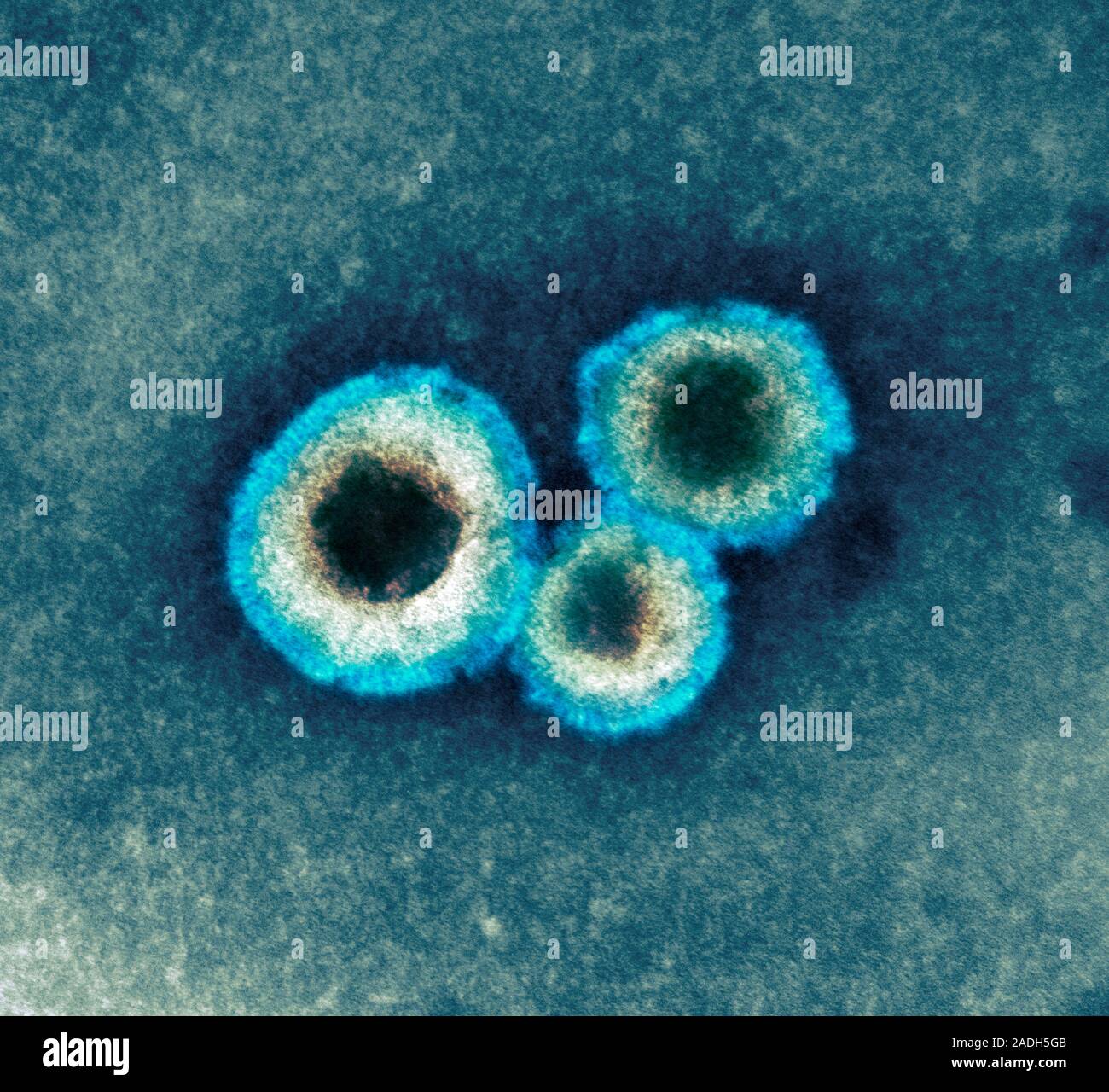
Human metapneumovirus particles. Coloured transmission electron - Source www.alamy.com

HMPV test Human Metapneumovirus Antigen test cassette - China medical - Source testsea.en.made-in-china.com
The Growing Threat Of Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) Infections In China
Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a common respiratory virus that can cause a range of illnesses, from mild upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) to severe lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia. hMPV is the second leading cause of hospitalization for LRTIs in children under 5 years of age in China, and the leading cause of hospitalization for LRTIs in infants under 1 year of age.

Human Metapneumovirus: China faces HMPV outbreak - should other - Source www.theasianaffairs.com
The incidence of hMPV infections has been increasing in China in recent years, and this is likely due to a number of factors, including increased urbanization, air pollution, and changes in climate. The increasing incidence of hMPV infections is a major public health concern, as it can lead to significant morbidity and mortality, particularly in young children.
There is no specific treatment for hMPV infection, and management is supportive. Ribavirin, an antiviral medication, has been shown to be effective in reducing the severity of hMPV infection in some studies, but it is not widely used in China. Palivizumab, a monoclonal antibody, is effective in preventing hMPV infection in high-risk infants, but it is also not widely used in China.
The development of new vaccines and antiviral therapies for hMPV is urgently needed. In the meantime, public health measures such as hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and staying home when sick can help to reduce the spread of hMPV infection.
Conclusion
hMPV infection is a major public health problem in China, and the incidence is increasing. There is no specific treatment for hMPV infection, and management is supportive. The development of new vaccines and antiviral therapies for hMPV is urgently needed.
In the meantime, public health measures such as hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and staying home when sick can help to reduce the spread of hMPV infection.